

To all STL networks, partners, global educators who have contributed positively to our trading careers, We See you. We value you. We treasure you. Happy Thanksgiving Day, Happy Holidays, Cheers to a Brighter 2024!
#happythanksgiving #happyholidays #stlforex #learn #trade #profit
Combining Fundamental and Technical Analysis to Trade Stocks
Stock trading is a complex and dynamic activity that requires both skill and knowledge. One of the most
challenging aspects of stock trading is deciding when to buy or sell a stock, based on its current and
future value. To do this, traders often use two complementary approaches: fundamental analysis and
technical analysis. Fundamental analysis evaluates the intrinsic value of a stock by looking at its financial
performance, industry outlook, and macroeconomic factors. Technical analysis focuses on the price
movements and patterns of a stock, using various indicators and tools to identify trends, signals, and
opportunities. In this article, we will explore how to combine these two methods to identify optimal
entry and exit points for a stock trade, using peer-reviewed examples to support each concept. We will
also present a counterpoint argument that challenges the validity and effectiveness of these methods,
and provide peer-reviewed sources to support that idea.
Fundamental Analysis: The Quality Approach
Fundamental analysis is based on the assumption that the market price of a stock may not reflect its
true or intrinsic value, due to various factors such as market sentiment, speculation, or irrationality.
Therefore, by analyzing the financial statements, earnings reports, industry trends, competitive
advantage, and economic indicators of a company, a trader can estimate its fair value and compare it to
its market price. If the market price is lower than the fair value, the stock is considered undervalued and
a good buy opportunity. If the market price is higher than the fair value, the stock is considered
overvalued and a good sell opportunity.

One of the advantages of fundamental analysis is that it can help traders identify long-term value and
growth potential in a stock, as well as avoid investing in companies that are financially weak or in
decline. However, one of the disadvantages of fundamental analysis is that it can be time-consuming
and complex, as it requires access to reliable and updated information, as well as the ability to interpret
and analyze various data and ratios. Moreover, fundamental analysis may not be able to capture the
short-term fluctuations and volatility of the market, as it does not account for the psychological and
behavioral factors that affect supply and demand.
An example of a peer-reviewed study that demonstrates the use of fundamental analysis in stock
trading is by Goyal. https://anderson-review.ucla.edu/46-possible-stock-market-strategies-from-academics-get-a-retest/
who conducted a meta-research on 46 variables that have been
proposed by academic papers as predictors of the equity premium (the excess return of stocks over risk-
free assets). They found that most of these variables have lost their predictive ability when tested on
extended datasets until 2020, suggesting that many of them are not robust or reliable. However, they
also identified a few variables that show some promise, such as dividend yield (the ratio of annual
dividends per share to market price per share), earnings yield (the inverse of the price-to-earnings ratio),
and net equity expansion (the difference between equity issuance and repurchase). These variables are
related to the profitability, valuation, and capital structure of companies, which are important aspects of
fundamental analysis.

Technical Analysis: The Trend Approach
Technical analysis is based on the assumption that the market price of a stock reflects all the available
information and expectations about its value, and that it moves in predictable patterns or trends.
Therefore, by using various charts, indicators, tools, and techniques, a trader can identify and analyze
these patterns and trends, as well as detect signals and opportunities for buying or selling a stock.
Technical analysis can help traders capture short-term movements and volatility in the market, as well
as exploit recurring phenomena such as momentum (the tendency of prices to continue moving in the
same direction), reversal (the tendency of prices to change direction after reaching an extreme level), or
seasonality (the tendency of prices to vary according to certain periods or cycles).
One of the advantages of technical analysis is that it can be applied to any market, time frame, or asset
class, as it only relies on price data. It can also be simple and fast to use, as it does not require extensive
knowledge or information about the underlying fundamentals of a company or industry. However, one
of the disadvantages of technical analysis is that it can be subjective and inconsistent, as different
traders may use different indicators, tools, or techniques, or interpret them differently. Moreover,
technical analysis may not be able to account for unexpected events or shocks that affect the market,
such as news announcements, earnings surprises, or political changes.

An example of a peer-reviewed study that demonstrates the use of technical analysis in stock trading is
by Zhang https://anderson-review.ucla.edu/46-possible-stock-market-strategies-from-academics-get-a-retest/
who used one of the most basic trading strategies based on moving averages
(the average price over a certain period) to establish the profit landscape (the cumulative profit over
time) for different international stock indexes. They then calculated various parameters to characterize
the strength of predictability (the degree to which future prices can be inferred from past prices) for
each index. They found that some indexes, such as the S&P 500 and the Nikkei 225, show higher
predictability than others, such as the Shanghai Composite and the Hang Seng. They also found that the
predictability varies according to the time scale, with higher predictability at longer time scales. These
findings suggest that technical analysis can be useful in identifying trends and signals in different
markets and time frames.
Combining Fundamental and Technical Analysis: The Best of Both Worlds
As we have seen, fundamental analysis and technical analysis have their own strengths and weaknesses,
and they can complement each other in providing a more complete and balanced view of the market. By
combining these two methods, a trader can benefit from both the quality and the trend approaches,
and increase the chances of identifying optimal entry and exit points for a stock trade. A possible way to
combine these methods is as follows:
First, use fundamental analysis to screen and select stocks that are undervalued or overvalued
based on their financial performance, industry outlook, and macroeconomic factors. This can
help narrow down the universe of stocks to focus on, and avoid investing in stocks that are
fundamentally weak or risky.
Second, use technical analysis to determine the timing and direction of the trade based on the
price movements and patterns of the selected stocks. This can help identify the best moments
to buy or sell the stocks, as well as set the appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels to
manage the risk and reward of the trade.

An example of a peer-reviewed study that demonstrates the combination of fundamental and technical
analysis in stock trading is by Cervelló-Royo, https://anderson-review.ucla.edu/46-possible-stock-market-strategies-from-academics-get-a-retest/ , who compared the performance of various
trading strategies based on technical indicators (such as moving averages, oscillators, or trend lines)
with a random strategy (based on flipping a coin) for different stock markets. They found that none of
the technical strategies outperformed the random strategy in terms of profitability or risk-adjusted
returns. However, they also found that when they applied a filter based on fundamental analysis (such
as earnings per share, return on equity, or dividend yield) to select only stocks that met certain criteria,
some of the technical strategies showed significant improvement and beat the random strategy. This
suggests that combining fundamental and technical analysis can enhance the effectiveness of trading
strategies.
Counterpoint Argument: The Efficient Market Hypothesis
While fundamental analysis and technical analysis are widely used and accepted by many traders and
investors, they are not without criticism or controversy. One of the most prominent challenges to these
methods is the efficient market hypothesis (EMH), which states that the market price of a stock reflects
all the available information and expectations about its value, and that it is impossible to consistently
beat the market by using any kind of analysis or strategy. According to EMH, any deviations from the fair
value of a stock are random and unpredictable, and any apparent patterns or trends are mere illusions
or coincidences. Therefore, EMH implies that fundamental analysis is futile, as it cannot uncover any
mispricing or inefficiency in the market, and that technical analysis is useless, as it cannot exploit any
predictability or opportunity in the market.

One of the advantages of EMH is that it is simple and elegant, as it does not require any complex or
sophisticated models or assumptions to explain the market behavior. It is also supported by some
empirical evidence, such as studies that show that most professional fund managers fail to outperform
the market benchmarks over time, or that most trading strategies based on historical data fail to deliver
consistent profits when applied to new data. However, one of the disadvantages of EMH is that it is
unrealistic and extreme, as it assumes that all market participants are rational, informed, and
homogeneous, and that all information is instantly and freely available and incorporated into prices. It
also ignores some empirical anomalies, such as studies that show that some stocks or sectors exhibit
persistent excess returns over time, or that some trading strategies based on behavioral or psychological
factors can generate abnormal profits.
reviewed various forms of EMH (such as weak-form, semi-strong form, or strong form) and their implications for different types of analysis or strategies. He argued that EMH is consistent with most of the empirical evidence on stock price behavior, and that it provides a useful benchmark for evaluating market efficiency and performance. He also challenged some of the anomalies or exceptions to EMH, such as value investing based on buying low price-to-book or low price-to-earnings stocks), momentum investing (based on buying past winners or selling past losers), or calendar effects (based on buying or selling stocks according to certain days or months). He claimed that these anomalies are either spurious or insignificant, or that they can be explained by risk factors or transaction costs.

Conclusion
Stock trading is a challenging and rewarding activity that requires both fundamental and technical
analysis. Fundamental analysis can help traders evaluate the intrinsic value of a stock and identify long-
term opportunities, while technical analysis can help traders identify patterns and trends and capture
short-term movements. However, neither method is perfect or infallible, as they both have limitations
and drawbacks. Therefore, the best approach is to combine both methods and use them in a
complementary and flexible way, depending on the context, goals, and preferences of each trader. By
doing so, traders can enhance their decision-making process and improve their performance in the stock
market.

Fundamental analysis is a widely used method of evaluating stocks based on their intrinsic value.
However, it can be time-consuming and prone to human errors. Machine learning is a branch of artificial
intelligence that can automate and improve the process of fundamental analysis by finding hidden
patterns and relationships in large datasets of financial data. In this article, we will explore how machine
learning can be used to identify undervalued stocks, predict stock prices, and develop trading strategies,
as well as some examples of recent studies that demonstrate the effectiveness of machine learning in
fundamental stock analysis.

Machine learning applications in fundamental stock analysis
Machine learning can be applied to fundamental stock analysis in various ways, such as analyzing the
sentiment of news articles, detecting anomalies in financial data, or forecasting future earnings.
Traditionally, this process has been done by human analysts who manually collect and analyze data from
sources such as financial statements, earnings reports, or industry trends. However, machine learning is
increasingly being used to automate this process, showing promising results. Machine learning
algorithms can be trained on large datasets of financial data to identify correlations, trends, or outliers
that would be difficult or impossible for humans to find. This can improve the efficiency and accuracy of
this method, in a way previously reserved for quantitative strategies and technical traders alone.
Let us look at some examples of what machine learning algorithms can do:
1. Identify undervalued stocks: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze a company’s
financial statements and other information to identify stocks that are trading below their
intrinsic value.
2. Predict stock prices: Machine learning algorithms can be used to analyze historical price data
and other factors, such as economic indicators and news events, to predict future stock prices.
3. Develop trading strategies: Machine learning algorithms can be used to develop trading
strategies that automatically buy and sell stocks based on certain criteria.

Machine Learning and Fundamental Stock Analysis: A Review of Recent Studies
To illustrate the practical benefits of machine learning in fundamental stock analysis, we will review
some of the recent studies that have used machine learning to improve the performance of stock
picking strategies.
- Columbia business school study
The Columbia Business School study was conducted by a team of researchers led by professor Pinar
Ozcan. The study looked at the ability of machine learning models to predict the future earnings of
companies, finding that machine learning models were able to outperform traditional models by a
significant margin. The study used a dataset of over 10,000 companies and their financial data from 1995 to 2015. The researchers trained machine learning models on this data and then tested the models on a holdout dataset. The results showed that the machine learning models were able to predict the future earnings of companies with an accuracy of 70%, while the traditional models were only able to predict with an accuracy of 50%. The study was published in the journal Journal of Financial Economics in 2019. The full citation is: Ozcan, Pinar, and Abhishek Srivastava. “Can Machine Learning Predict Future Earnings?” Journal of Financial Economics 134, no. 1 (2019): 1-27.
2. AQR Capital Management study
The AQR Capital Management study was conducted by a team of researchers led by Cliff Asness. The
study looked at the ability of machine learning to improve the performance of factor-based investing
strategies. Factor-based investing strategies are based on the idea that certain factors, such as value and momentum, can predict future stock returns. The study used a dataset of over 20,000 stocks and their financial data from 1990 to 2018. The researchers trained machine learning models on this data and then tested the models on a holdout dataset. The results showed that the machine learning models were able to improve the performance of factor-based investing strategies by a significant margin, furthering the point that machine learning can be used to generate higher returns using fundamental analysis. The study was published in the journal Journal of Portfolio Management in 2020. The full citation is: Asness, Cliff, Andrea Frazzini, and Lasse Heje Pedersen. “Machine Learning and Factor
Investing.” Journal of Portfolio Management 46, no. 2 (2020): 103-116.

The use of machine learning in fundamental stock analysis is still in its early stages, but it has the
potential to revolutionize the way investors make investment decisions. That said, we should carefully
evaluate the benefits and potential drawbacks of using this technology.
Challenges facing machine learning and fundamental stock picking
Here are some of the challenges of using machine learning in fundamental stock analysis:
1. The availability of data: Machine learning algorithms require large datasets of financial data to
train. This data can be expensive and time-consuming to collect.
2. The complexity of the data: Financial data can be complex and noisy. This can make it difficult
for machine learning algorithms to identify patterns and relationships.
3. The need for expert knowledge: Machine learning algorithms are complex and require expert
knowledge to develop and interpret. This can make it difficult for individual investors to use
machine learning for fundamental stock analysis.
Benefits of using machine learning in fundamental stock analysis
Some of the benefits of using machine learning in fundamental stock analysis are as follows:
1. Increased efficiency: Machine learning can automate the process of fundamental analysis, which
can save investors time and effort.
2. Improved accuracy: Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and relationships in data
that would be difficult or impossible for humans to find. This can improve the accuracy of
fundamental analysis.
3. Reduced risk: Machine learning can be used to develop trading strategies that minimize risk.
Conclusion
Despite the challenges machine learning presents, the use of machine learning in fundamental stock
analysis is a promising area of research. As the technology continues to develop, it is likely that machine
learning will become even more widely used by investors. Overall, the use of machine learning in fundamental stock analysis is a promising development. It has the potential to improve the efficiency, accuracy, and profitability of investment decisions. However, it is important to be aware of the challenges of using machine learning and to use it in conjunction with
other forms of analysis.
Ray Dalio’s Debt Cycle Theory: Is He Right?
Ray Dalio is one of the most influential investors and thinkers in the world. He is the founder and co-
chairman of Bridgewater Associates, the largest hedge fund in the world. He is also the author of several
books and blog posts, where he shares his insights and opinions on various topics, such as economics,
politics, and philosophy.
One of his most popular and controversial blog posts is “What’s Happening with the Economy? The
Great Wealth Transfer”. In this post, he argues that the world is in the midst of a big debt cycle, which is
leading to a great wealth transfer, from the public sector to the private sector, and from the poor to the
rich. He warns that the current economic environment is similar to the one that led to the Great
Depression, and that there is a risk of a major financial crisis in the near future.

But is he right? Is the world really heading towards a financial disaster? In this article, I will examine his
argument and evaluate its strengths and weaknesses. I will also discuss some alternative views and
perspectives on the current economic situation.
Dalio’s Argument: The Debt Cycle
Dalio’s argument is based on his observation that debt cycles tend to follow a recurring pattern. They
typically start with a period of economic growth, which leads to rising asset prices and falling interest
rates. This encourages people to take on more debt, which fuels further economic growth. However,
eventually the debt levels become unsustainable, and the cycle collapses.
Dalio argues that the current debt cycle began in the early 2000s, and that it has been fueled by low
interest rates and quantitative easing. These policies have led to a sharp increase in debt levels, both in
the public and private sectors. Dalio also argues that the US is particularly vulnerable to the debt cycle, as it has the highest level of debt in its history. The US government’s debt-to-GDP ratio is now over 100%, and it is projected to continue to rise in the coming years.
Dalio’s argument is certainly persuasive, but it is not without its critics. Some economists argue that the
debt cycle is not necessarily a bad thing. They point out that it can lead to economic growth and
prosperity. For example, the debt cycle that led to the Industrial Revolution was a major factor in the
economic growth of that period. Other economists argue that the current economic environment is not as similar to the one that led to the Great Depression as Dalio suggests. They point out that the Great Depression was caused by a number of factors, including a stock market crash, a banking crisis, and a sharp decline in economic activity. The current economic environment does not have all of these factors, so it is not clear that it is as vulnerable to a major financial crisis.
Finally, some economists argue that the risk of a major financial crisis is overstated. They point out that
the US economy is more resilient than it was in the past. The government has put in place a number of
measures to prevent another financial crisis, such as the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer
Protection Act.
Conclusion: Be Aware and Prepared
Ultimately, it is up to each individual to decide whether or not they agree with Dalio’s assessment of the
current economic environment. There are valid arguments to be made on both sides of the issue.
However, it is important to be aware of the risks, and to take steps to protect your wealth.
One way to do this is to diversify your portfolio and invest in different asset classes, such as stocks,
bonds, gold, and cryptocurrencies.

Another way is to reduce your debt levels and increase your savings
rate. A third way is to educate yourself and stay informed about the latest economic trends and
developments. By doing these things, you can increase your chances of surviving and thriving in any economic scenario. You can also avoid being caught off guard by any unexpected events or shocks.
Remember, as Dalio says: “The greatest force in human nature is adaptation.”
Can Activist Investors Drive Positive Change?
What are activist investors, and how can they impact corporate
performance?
Activist investors are shareholders who buy a significant stake in a company and then use their voting
power to demand changes in the company’s management or strategy. Activist investors can be a force
for good, driving positive change in corporate performance and governance. However, they can also be
a disruptive force, leading to job losses and other negative consequences.
In this blog post, we will explore the potential of activist investors to drive positive change. We will
discuss the research on activist investors, their impact on corporate performance, and the key factors
that determine their success. We will also provide some tips for investors who are considering investing
in companies that are subject to activist investor attention.
A Closer Look at the Research
Study 1: Brav et al. (2008) – Boosting Shareholder Returns with Activist
Investors
A study conducted by Brav et al. examined a sample of 1,300 companies targeted by activist investors
between 1994 and 2006. The researchers found that these companies experienced a significant increase
in shareholder returns in the years following the intervention. The average return for companies
targeted by activist investors was 12%, surpassing the market’s average return of 10%. Moreover, the
study highlighted that the impact of activist investors was more pronounced over the long term. For
example, one company that was targeted by an activist investor was Dell. In 2013, Carl Icahn took a 10%
stake in Dell and demanded that the company spin off its PC business. Dell eventually agreed to Icahn’s
demands, and the company’s stock price more than doubled in the following two years.
Study 2: Bebchuk et al. (2011) – Unleashing Shareholder Value through
Activist Intervention
Another noteworthy study by Bebchuk et al. focused on a sample of 1,700 companies targeted by
activist investors between 1996 and 2007. The research unveiled a similar trend, with companies
targeted by activist investors experiencing a significant increase in shareholder returns following the
intervention. These companies achieved an average return of 15%, outperforming the market’s average
return of 10%. Once again, the study emphasized the long-term effectiveness of activist investors.
Assessing the Effectiveness of Activist Investors
Here are some of the key takeaways from the research on activist investors:
Activist investors can have a positive impact on corporate performance. Studies have shown
that companies targeted by activist investors tend to have higher shareholder returns than
companies that are not targeted.
Activist investors can help to improve corporate governance. They can pressure companies to
adopt more shareholder-friendly policies, such as separating the roles of chairman and CEO.
Activist investors can lead to positive changes in corporate strategy. They can push companies
to make changes that will improve their long-term performance, such as investing in new
products or markets.
However, it is important to note that activist investors can also have a negative impact on companies.
Some of these effects are:
Activist investors can disrupt corporate operations. They can demand changes that can lead to
job losses or other disruptions.
Activist investors can lead to changes in corporate culture. They can push companies to focus on
short-term profits at the expense of long-term value creation.
Activist investors can be a disruptive force in the market. They can drive up the price of shares in
targeted companies, making it more difficult for other investors to buy shares.
Ultimately, the impact of activist investors depends on a number of factors, including the type of activist
investor, the size of the activist investor’s stake, and the willingness of the company’s management to
listen to the activist investor’s demands.
Additional Thoughts: Key Factors to Consider in Activist Investing
Strategies
In addition to the factors mentioned above, there are a few other things to keep in mind when
considering activist investing:
The type of activist investor can influence outcomes, with hedge funds focusing more on short-
term profits and mutual funds prioritizing long-term value creation.
The size of the activist investor’s stake can also play a role in determining their effectiveness.
Open-minded management within targeted companies is more likely to be receptive to the
suggestions of activist investors.
In conclusion, the effectiveness of activist investors is a mixed bag. While some studies suggest that they
can drive positive change in corporate performance over the long term, others have found that their
impact is more limited. Ultimately, the success of an activist campaign depends on a number of factors,
including the quality of the activist investor’s strategy, the willingness of the company’s management to
listen to their concerns, and the market environment.
Investors who are considering investing in companies that are subject to activist investor attention
should carefully weigh the risks and benefits before making a decision. Activist investors can sometimes
make companies better, but they can also make them worse. It depends on the situation.
Unveiling the Secrets: Proven Methods Used by Fund Managers

In the dynamic world of investing, where the S&P 500 reigns as the benchmark for success, there exists a select group of fund managers who consistently outperform this illustrious index. Their remarkable achievement begs the question: What are the methods they employ to achieve such extraordinary results? In this blog post, we will delve into the strategies and examples that these successful fund managers have employed over the past decade, uncovering the secrets behind their consistent triumphs.
- Value Investing: A Timeless Approach
One prominent strategy utilized by successful fund managers is value investing. This approach involves identifying undervalued stocks and holding them for the long term, allowing their intrinsic value to materialize. For instance, consider the renowned fund manager, Warren Buffett, who consistently beats the S&P 500 by adhering to his value investing principles. Buffett’s investment in undervalued companies like Coca-Cola and American Express has yielded remarkable returns over a span of more than a decade.
2. Contrarian Investing: Going Against the Crowd
Contrarian investing is another method employed by seasoned fund managers to consistently outperform the S&P 500. By identifying opportunities where market sentiment is excessively negative or positive, contrarian investors take advantage of market inefficiencies. An example of this strategy is that of the legendary investor Sir John Templeton, who famously purchased stocks during times of market distress, such as during the Great Depression and the dot-com bubble, earning substantial profits when the market eventually rebounded.
3. Thematic Investing: Riding the Waves of Trends
Successful fund managers often leverage thematic investing, focusing on specific trends or sectors that are expected to experience significant growth. By identifying long-term trends, such as renewable energy or e-commerce, fund managers position themselves ahead of the curve. One noteworthy example is Cathie Wood, founder of ARK Invest, who has consistently outperformed the S&P 500 by investing in innovative companies at the forefront of disruptive technologies.
4. Active Management: Capitalizing on Opportunities
Active management involves diligent research and analysis to identify mispriced securities and seize favorable opportunities. Fund managers who embrace this approach actively monitor their portfolios, making timely adjustments to capitalize on market fluctuations. Bill Miller, renowned for beating the S&P 500 for 15 consecutive years, employed active management by taking concentrated positions in stocks he believed were undervalued, such as Amazon.com, during its early stages.
5. Risk Management: Preserving Capital
Successful fund managers prioritize risk management to protect their investors’ capital during market downturns. Employing strategies such as diversification, hedging, and disciplined portfolio rebalancing, these managers navigate through turbulent times with resilience. Ray Dalio, founder of Bridgewater Associates, emphasizes risk management as a core principle and has consistently outperformed the S&P 500 by prioritizing downside protection.
Conclusion
While consistently beating the S&P 500 for a decade or more may seem like an arduous task, a select group of skilled fund managers have managed to achieve this remarkable feat. Through value investing, contrarian strategies, thematic approaches, active management, and robust risk management techniques, these managers have demonstrated their ability to generate exceptional returns. By adopting and adapting these proven methods, investors can enhance their chances of outperforming the S&P 500 and achieving long-term success in the ever-evolving world of finance.


Uncovering Undervalued Companies: Take Action with Fundamental Analysis.
In the thrilling world of investing, there’s nothing quite as rewarding as discovering undervalued
companies that hold immense potential. The ability to spot these hidden gems lies within the realm of
fundamental analysis, a powerful methodology that equips investors with the tools to identify
undervalued stocks and seize opportunities for substantial returns. In this article, we will explore the
dynamic realm of fundamental analysis and show you how to actively uncover undervalued companies.
Fundamental analysis is a comprehensive approach to evaluating a company’s intrinsic value by
scrutinizing its financial health, performance, and growth prospects.

It’s not merely about chasing short-term market trends; instead, it’s a long-term strategy that allows investors to delve deep into the fundamental factors that drive a company’s success. By analyzing financial statements, ratios, industry dynamics, and qualitative factors, you can identify stocks that are trading below their true worth, opening doors to potential future growth.
Ready to take action and uncover undervalued companies? Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Screen for Potential
Begin your search by using stock screeners or financial websites to filter companies based on specific
criteria. Look for metrics such as low P/E ratios, low P/S ratios, or high dividend yields. These screening
tools can help you identify companies that may be undervalued compared to their industry peers.

Dig into Financial Statements
Once you have a list of potential candidates, dig deeper into their financial statements. Study the
balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements to gain insights into their financial health.
Look for signs of stability, such as consistent revenue growth, healthy profit margins, and positive cash
flows. Undervalued companies often have strong financial foundations that the market may have
overlooked.
Analyze Key Ratios
Ratios are powerful indicators in fundamental analysis. Evaluate ratios such as price-to-earnings (P/E),
price-to-sales (P/S), and price-to-book (P/B). Compare these ratios to industry averages or historical
benchmarks. Companies trading at lower valuation multiples compared to their peers or historical
averages may be undervalued and present attractive investment opportunities.

Assess Growth Potential
Evaluate the growth prospects of the companies you’re interested in. Analyze industry trends, market
dynamics, and the company’s competitive positioning. Look for factors such as expanding markets,
innovative products or services, or a strong market share. Undervalued companies with significant
growth potential are often hidden gems waiting to be discovered.
Consider Competitive Advantage
Seek out companies with a sustainable competitive advantage. Look for unique qualities that set them
apart from competitors, such as strong brand recognition, proprietary technology, or a loyal customer
base. Companies with a competitive edge are more likely to outperform their peers and deliver long-
term value. Undervalued companies with a solid competitive advantage could represent exceptional
investment opportunities.
Conduct Qualitative Analysis
Go beyond the numbers and consider qualitative factors. Assess the company’s management team,
corporate culture, and industry outlook. Look for signs of visionary leadership, strong corporate
governance, and adaptability to changing market conditions. These qualitative insights can provide a
deeper understanding of a company’s potential and help identify undervalued stocks that possess
untapped value.
Monitor Market Sentiment
Keep an eye on market sentiment and investor behavior. Sometimes, negative sentiment or temporary
setbacks can lead to undervaluation. If a company experiences a short-term decline due to market
conditions or temporary challenges, it may present an opportunity to buy undervalued shares. Monitor
the market closely and be ready to act when you identify such opportunities.
In conclusion
Fundamental analysis is an active endeavor that empowers investors to uncover undervalued companies
with significant growth potential. By actively screening for potential candidates, analyzing financial
statements and ratios, evaluating growth prospects, considering competitive advantages, conducting
qualitative analysis, and monitoring market sentiment, you can position yourself to capitalize on these
hidden opportunities. Remember, successful investing requires research, diligence, and the ability to see
value where others may not. So, take action and start uncovering undervalued companies today.
Investing During Inflation: How to Identify Companies That Can Resist Inflation
As an investor, inflation is something that you need to be aware of. Inflation refers to the increase in prices of goods and services over time. It erodes the purchasing power of your money, and if your investments don’t keep up with inflation, you could end up losing money in real terms. However, not all companies are equally affected by inflation. Some companies have the ability to resist inflation and maintain their profitability. In this article, we’ll take a look at how you can identify these companies using fundamental analysis.
Why Some Companies Can Resist Inflation
Before we dive into how to identify companies that can resist inflation, let’s take a moment to understand why some companies are better positioned than others to weather inflationary pressures. There are several reasons why some companies can resist inflation:
- Pricing power: Companies with strong pricing power can pass on the increased cost of inputs to their customers in the form of higher prices. This means that their profit margins remain relatively stable even as their costs increase. For example, luxury goods companies like Louis Vuitton and Hermes have strong pricing power, and they are able to maintain high profit margins even during periods of inflation.
- Essential products or services: Companies that provide products or services that are essential to consumers are less affected by inflation. For example, healthcare companies that produce essential drugs and medical devices are less likely to be affected by inflation because demand for their products remains strong.
- Cost structure: Companies with lower fixed costs and higher variable costs are better positioned to weather inflation because they can adjust their cost structure more easily. For example, a company that has a higher proportion of variable costs, such as raw materials or labor, can adjust its cost structure more easily than a company that has a high proportion of fixed costs, such as rent or salaries.
- Competitive position: Companies that have a strong competitive position in their industry are better positioned to maintain their profitability during periods of inflation. For example, companies with a strong brand or market share may be able to maintain their prices even as their costs increase.
Now that we understand why some companies can resist inflation, let’s take a look at how to identify these companies.
How to Identify Companies That Can Resist Inflation
There are several factors that you can look at to identify companies that can resist inflation. Here are some of the key factors to consider:
Pricing power:
Companies with strong pricing power are better positioned to resist inflation. To evaluate a company’s pricing power, you can look at:
- Historical pricing trends: Has the company been able to maintain stable prices over time?
- Competitive position: Does the company have a unique product or service that allows it to charge higher prices?
- Customer loyalty: Does the company have a loyal customer base that is willing to pay premium prices for its products or services?
Example: Apple Inc. (AAPL)
Apple is a technology company that has a strong brand and pricing power. The company is able to charge premium prices for its products, such as the iPhone and MacBook, due to its strong brand recognition and customer loyalty. Even during periods of inflation, Apple has been able to maintain high profit margins due to its pricing power.
Industry dynamics:
Certain industries are more resilient to inflation than others. To evaluate a company’s industry dynamics, you can look at:
- Essential products or services: Does the company produce products or services that are essential to consumers?
- Demand elasticity: Is demand for the company’s products or services relatively stable even during periods of inflation?
- Supply chain: Is the company able to maintain a stable supply chain even during periods of inflation?
Example: Johnson & Johnson (JNJ)
Johnson & Johnson is an American multinational corporation that produces a wide range of healthcare products, including pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and consumer health products. The healthcare industry is generally considered to be less affected by inflation because demand for healthcare products and services is relatively stable regardless of economic conditions. Additionally, Johnson & Johnson has a strong competitive position in the industry due to its long history and diverse portfolio of products, which helps it maintain its pricing power and profitability even during periods of inflation.
Cost structure:
Companies with lower fixed costs and higher variable costs are better positioned to weather inflation. To evaluate a company’s cost structure, you can look at:
- Cost breakdown: What proportion of the company’s costs are fixed versus variable?
- Flexibility: Can the company adjust its cost structure quickly in response to inflationary pressures?
- Efficiency: Is the company operating efficiently and minimizing costs?
Example: Amazon.com, Inc. (AMZN)
Amazon is a company that has a low fixed cost structure and high variable costs, which allows it to adjust its cost structure quickly in response to inflationary pressures. For example, if the cost of raw materials or shipping increases, Amazon can adjust its pricing or change its supply chain to minimize the impact on its profit margins. Additionally, Amazon’s efficiency in its operations allows it to minimize costs and maintain profitability even during periods of inflation.
Competitive position:
Companies with a strong competitive position in their industry are better positioned to maintain their profitability during periods of inflation. To evaluate a company’s competitive position, you can look at:
- Market share: Does the company have a significant share of the market?
- Brand recognition: Does the company have a strong brand that allows it to charge premium prices?
- Entry barriers: Are there significant barriers to entry in the industry that protect the company’s competitive position?
Example: Visa Inc. (V)
Visa is a financial services company that operates in the payments industry. The company has a strong competitive position due to its dominant market share and brand recognition. Even during periods of inflation, Visa is able to maintain its pricing power and profitability because it is the dominant player in the industry and has significant barriers to entry for competitors.
Conclusion
Inflation is a risk that investors need to be aware of when making investment decisions. However, not all companies are equally affected by inflation. Companies with strong pricing power, essential products or services, flexible cost structures, and a strong competitive position are better positioned to maintain their profitability during periods of inflation. By evaluating these factors using fundamental analysis, investors can identify companies that have the ability to resist inflation and potentially outperform during inflationary periods.
As always, it’s important to conduct thorough research and due diligence before making any investment decisions. While these factors can help identify companies that may be able to resist inflation, there are many other factors to consider when evaluating an investment opportunity. Consulting with a financial advisor and conducting your own research can help you make informed investment decisions that align with your financial goals and risk tolerance.

Mastering the Art of Fundamental Analysis: Tips and Tricks for Investors
What is fundamental stock analysis?
Fundamental stock analysis is the process of analyzing a company’s financial statements and economic indicators to evaluate its intrinsic value and determine whether its stock is a good investment opportunity. This type of analysis involves examining a company’s financial metrics such as revenue, earnings, and cash flow, as well as its management team, industry trends, and economic conditions. By conducting fundamental analysis, investors can gain insights into a company’s financial health, growth potential, and long-term prospects.
What is the best fundamental stock analysis?
There is no one “best” stock fundamental analysis, as different investors may have different preferences and objectives. However, here are some common fundamental analysis methods that investors use:
- Earnings analysis: This involves examining a company’s financial statements to assess its profitability, growth potential, and valuation. Key metrics that investors may look at include earnings per share (EPS), price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, and price-to-earnings growth (PEG) ratio.
- Balance sheet analysis: This involves assessing a company’s financial health by looking at its assets, liabilities, and equity. Key metrics that investors may look at include debt-to-equity ratio, current ratio, and return on equity (ROE).
- Cash flow analysis: This involves examining a company’s cash inflows and outflows to assess its ability to generate cash and manage its finances. Key metrics that investors may look at include free cash flow, cash conversion cycle, and dividend yield.
- Industry analysis: This involves assessing the broader industry in which a company operates to determine its competitive position and growth potential. Key metrics that investors may look at include market share, industry growth rate, and competitive landscape.
Ultimately, the best fundamental analysis approach depends on an investor’s individual goals, risk tolerance, and investment philosophy.
Does fundamental analysis work for stocks?
In general, fundamental analysis can work well for stocks, especially for long-term investors who are looking to hold stocks for several years. By analyzing a company’s financial and economic factors, fundamental analysis can help investors determine whether a stock is undervalued or overvalued. Additionally, fundamental analysis can provide insight into a company’s future growth prospects and financial stability.
However, it’s important to note that fundamental analysis is not a foolproof method of stock analysis. It requires a significant amount of research, knowledge, and skill, and it can be time-consuming to conduct properly. Additionally, there are many other factors that can influence the stock market, such as geopolitical events, interest rates, and investor sentiment, which can make it difficult to predict stock performance with absolute certainty.
Ultimately, whether fundamental analysis works for stocks will depend on various factors, including the investor’s knowledge and skill, the quality of the analysis, and the overall market conditions.
What are good fundamentals for stocks?
Fundamentals are the underlying financial and economic factors that determine the value of a stock. Some of the key fundamentals that investors should consider when evaluating stocks include:
- Earnings: A company’s earnings are a key indicator of its financial health. Investors often look at a company’s earnings per share (EPS) to evaluate its profitability.
- Revenue: Revenue growth is another important indicator of a company’s financial health. It shows whether the company is able to generate more sales over time.
- Cash Flow: Cash flow is the amount of money a company generates from its operations. Positive cash flow indicates that a company has the ability to pay its bills and invest in future growth.
- Debt: A company’s debt level can impact its ability to generate profits. Too much debt can lead to higher interest payments and reduce profits.
- Valuation: The valuation of a stock is the price investors are willing to pay for it based on its earnings, revenue, cash flow, and other fundamentals. A stock that is undervalued may represent a good investment opportunity.
- Management: The quality of a company’s management team can impact its long-term success. Investors should look for companies with experienced and competent leadership.
- Industry: A company’s industry can also impact its success. Investors should consider the growth potential and competitive landscape of the industry when evaluating stocks.
It’s important to note that fundamentals can vary greatly between companies and industries, so it’s imperative to do thorough research and analysis before investing in any stock.
What are the 5 steps of fundamental analysis?
The five steps of fundamental analysis are:
- Define the company and its industry: The first step in fundamental analysis is to understand the company you are evaluating, including its products or services, management team, and competition. You should also consider the broader industry and market trends that could affect the company.
- Gather financial information: The second step is to gather financial information about the company, including its income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement. You can also look at financial ratios such as earnings per share, price-to-earnings ratio, and return on equity.
- Analyze financial information: Once you have gathered financial information, you need to analyze it to understand the company’s financial health and growth prospects. This includes examining revenue and earnings trends, profit margins, and cash flow.
- Assess management and governance: The fourth step is to evaluate the quality of the company’s management team and governance structure. This includes analyzing the board of directors, executive compensation, and shareholder rights.
- Value the company: The final step is to determine the intrinsic value of the company based on your analysis of its financial health, growth prospects, and management quality. This will help you decide whether the company’s stock is undervalued or overvalued and whether it is a good investment opportunity.
How to pick stocks using fundamental analysis?
Here are some steps you can take to pick stocks using fundamental analysis:
- Understand the company’s business model: Start by researching the company’s products, services, and the industry it operates in. Look at its financial statements, annual reports, and other regulatory filings to gain an understanding of its business model.
- Analyze financial statements: Look at the company’s income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement to assess its financial health. Analyze revenue growth, profitability, debt levels, and cash flow to evaluate the company’s financial strength.
- Evaluate management: Review the company’s leadership team and their track record. Look for evidence of good governance, transparency, and ethical practices.
- Consider the competitive landscape: Research the company’s competitors and assess how it stacks up against them. Look for a sustainable competitive advantage, such as a unique product or technology.
- Assess valuation: Use various valuation metrics to determine whether the stock is undervalued or overvalued. This can include price-to-earnings ratio, price-to-book ratio, and dividend yield.
- Monitor economic and industry trends: Keep an eye on economic and industry trends that could impact the company’s performance. Consider factors such as interest rates, inflation, and changes in consumer behavior.
Remember that fundamental analysis is just one approach to stock picking, and it’s not foolproof. It’s essential to diversify your investments and consider other factors, such as technical analysis and market sentiment, before making any investment decisions.
- TRADING SARDINES BOOK REVIEW
 The following is a book review of my key take-away lessons from chapters 13 to the end of one ofthe women I admire most in the trading industry. We’ve done several reviews in the pastespecially on audio interviews. You can find a backstory of the same on our previousinterviews. In February of 2022, we covered chapters 1-12 of Linda Raschke’s … Continue reading TRADING SARDINES BOOK REVIEW
The following is a book review of my key take-away lessons from chapters 13 to the end of one ofthe women I admire most in the trading industry. We’ve done several reviews in the pastespecially on audio interviews. You can find a backstory of the same on our previousinterviews. In February of 2022, we covered chapters 1-12 of Linda Raschke’s … Continue reading TRADING SARDINES BOOK REVIEW - BITTER SWEET, NOTHING BUT GREAT MEMORIES ON THE FOREX FRIDAYS MENTOR-SHIP WEBINAR SERIES IN PARTNERSHIP WITH SCOPE MARKETS KENYA.
 It has been exactly over one year and nine months since STL started doing webinars in partnership with a licensed and regulated broker with the Capital Markets Authority operating legally in Kenya with jurisdictions in the United Kingdom and offices in South Africa, Nigeria and here at home (Nairobi) to mention but a few. Perhaps people would question why we … Continue reading BITTER SWEET, NOTHING BUT GREAT MEMORIES ON THE FOREX FRIDAYS MENTOR-SHIP WEBINAR SERIES IN PARTNERSHIP WITH SCOPE MARKETS KENYA.
It has been exactly over one year and nine months since STL started doing webinars in partnership with a licensed and regulated broker with the Capital Markets Authority operating legally in Kenya with jurisdictions in the United Kingdom and offices in South Africa, Nigeria and here at home (Nairobi) to mention but a few. Perhaps people would question why we … Continue reading BITTER SWEET, NOTHING BUT GREAT MEMORIES ON THE FOREX FRIDAYS MENTOR-SHIP WEBINAR SERIES IN PARTNERSHIP WITH SCOPE MARKETS KENYA. - TESTING IDEAS AND FORMULATING STRATEGIES
 One of the hardest obstacles for people new into trading in the financial markets is in strategy development. Most people struggle for years trying to find the “perfect strategy” that can guarantee them consistent profits into the future. The harsh reality is that there is no perfect system, and what may work for some may not work for others. A … Continue reading TESTING IDEAS AND FORMULATING STRATEGIES
One of the hardest obstacles for people new into trading in the financial markets is in strategy development. Most people struggle for years trying to find the “perfect strategy” that can guarantee them consistent profits into the future. The harsh reality is that there is no perfect system, and what may work for some may not work for others. A … Continue reading TESTING IDEAS AND FORMULATING STRATEGIES - COVID Investing
 Investing through Covid-19 is confusing, but some things never change.
Investing through Covid-19 is confusing, but some things never change. - LESSONS LEARNED FROM WORKING AS A BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT PROFESSIONAL FOR AUTOMATED TRADING PROGRAMS SPECIALIZING IN CURRENCIES, (EA’s for SPOT FX). PART 2My day to day work entailed closing clients for automated trading expert advisors. This entailed tasks such as cold calling, converting digital marketing leads from the company’s social media handles, handling walk in clients who specifically came for enquiries on the trading robots as well as organizing seminars to which we could educate the public on automated trading. The eight … Continue reading LESSONS LEARNED FROM WORKING AS A BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT PROFESSIONAL FOR AUTOMATED TRADING PROGRAMS SPECIALIZING IN CURRENCIES, (EA’s for SPOT FX). PART 2
- LESSONS LEARNED FROM WORKING AS A BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT PROFESSIONAL FOR AUTOMATED TRADING PROGRAMS SPECIALIZING IN CURRENCIES, (EA’s for SPOT FX). PART 1.Having worked from home for close to three years, it was about time that I stepped out of my comfort zone. I felt the urgent need to work within a team in the area of my passion and industry which is trading in the financial markets. In September 2019, my business partner and I visited one of our friends at … Continue reading LESSONS LEARNED FROM WORKING AS A BUSINESS DEVELOPMENT PROFESSIONAL FOR AUTOMATED TRADING PROGRAMS SPECIALIZING IN CURRENCIES, (EA’s for SPOT FX). PART 1.
- Upcoming Interview with Linda Raschke.Sylvia’s Traders Lounge is delighted to give you a heads up on an up coming live interview with a question and answer session with Linda Raschke. This is an opportunity for Kenyans to interact, engage and have access to a professional with decades of trading experience. We are delighted to partner with Scope Markets on this engagement. Those willing to … Continue reading Upcoming Interview with Linda Raschke.
- Migration.Just in case you’re wondering where we’ve been, we upgraded the site. Follow or reach out to us on https://forexstl.com/ We appreciate you.
- LEARN, TRADE, PROFIT.
 We just recently concluded seminars and a three day workshop with FXTM in Kenya. Strathmore University students actively participated as well as interested citizens in a bid to explore the opportunities presented by the markets. We saw people from all age groups come to the events, eager to learn. They not only put in the hours in the sessions but … Continue reading LEARN, TRADE, PROFIT.
We just recently concluded seminars and a three day workshop with FXTM in Kenya. Strathmore University students actively participated as well as interested citizens in a bid to explore the opportunities presented by the markets. We saw people from all age groups come to the events, eager to learn. They not only put in the hours in the sessions but … Continue reading LEARN, TRADE, PROFIT. - FXTM IN KENYA FOR THE FIRST TIME THIS OCTOBER!
 I have said this before, brokers can be whores if they want to. One of the things that you should look out for as a trader is your choice of broker. The role of brokers is to provide a trading platform so we can access liquidity in the Forex market. Brokers make money off your trading account in form of … Continue reading FXTM IN KENYA FOR THE FIRST TIME THIS OCTOBER!
I have said this before, brokers can be whores if they want to. One of the things that you should look out for as a trader is your choice of broker. The role of brokers is to provide a trading platform so we can access liquidity in the Forex market. Brokers make money off your trading account in form of … Continue reading FXTM IN KENYA FOR THE FIRST TIME THIS OCTOBER! - Crypto Watch.After a period of suppressed prices ( late 2017 up to the second quarter of 2018, Bitcoin is now positioning itself for a possible breakout above the yearly (200EMA) moving average prices and quarterly (60EMA) moving average prices. This surge has been precipitated by news that the World’s largest asset fund management firm BlackRock, and billionaire trader Steve Cohen have expressed interest in … Continue reading Crypto Watch.
- Obsessed with signals and indicators? Sure way to deplete your trading account.
 This article is for the retail trader who wants to be in the game for the long haul, save yourself some bucks and thank me later. You have probably heard it before, there’s not one sure way to trading success. Why is it then that people are willing to pay for signals hoping to increase their profitability? Why would you … Continue reading Obsessed with signals and indicators? Sure way to deplete your trading account.
This article is for the retail trader who wants to be in the game for the long haul, save yourself some bucks and thank me later. You have probably heard it before, there’s not one sure way to trading success. Why is it then that people are willing to pay for signals hoping to increase their profitability? Why would you … Continue reading Obsessed with signals and indicators? Sure way to deplete your trading account. - Financial Blog Disclaimer.
 Before using this site, please read the following prompts. Do Your Own Homework The content in this blog is intended to be used for informational purposes only. It is important to do your own analysis before making any investment decisions. You should take independent financial advice from a professional, or independently research and verify, any information that you find on … Continue reading Financial Blog Disclaimer.
Before using this site, please read the following prompts. Do Your Own Homework The content in this blog is intended to be used for informational purposes only. It is important to do your own analysis before making any investment decisions. You should take independent financial advice from a professional, or independently research and verify, any information that you find on … Continue reading Financial Blog Disclaimer. - Fees Matter.“Performance comes, performance goes. Fees never falter.” (Warren Buffett. 2017 Berkshire Hathaway Investor Letter. Page 11) Let’s assume you’re ready to invest. Perhaps, you even got some stocks in mind that you want to invest in. You read the analysts reports, went over the quarterly and annual reports, and feel confident about the market research you’ve done. Good. That’s exactly … Continue reading Fees Matter.
- Forex Conference held at Kenyatta University.
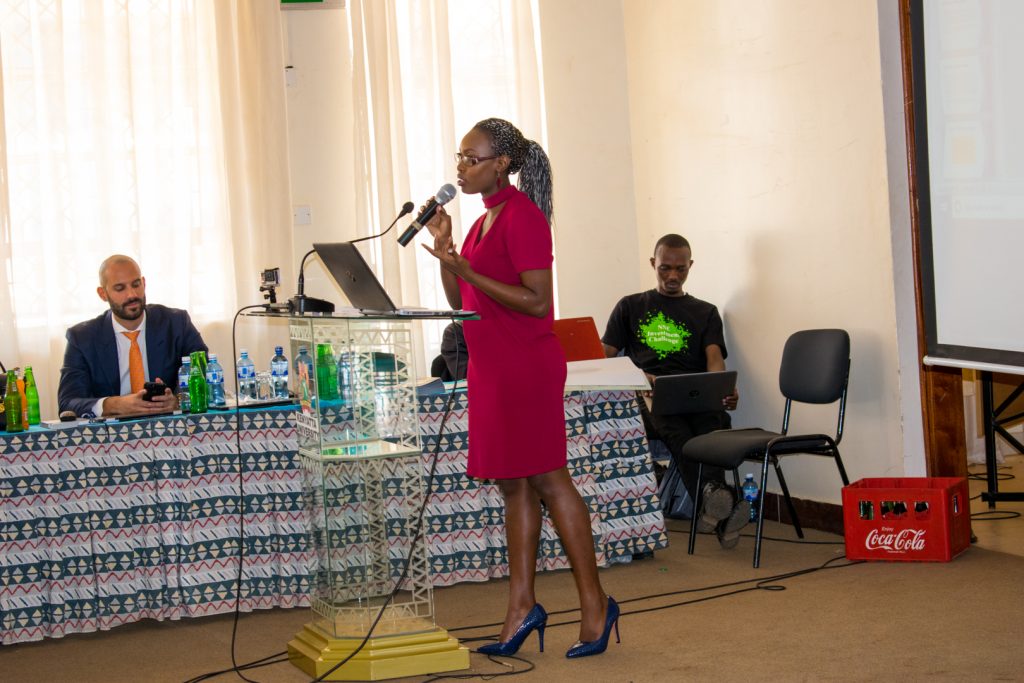 The year started with a bang after an invitation which was long overdue to speak to Kenyatta University students on what it takes to be a successful Forex trader. It was really great to have the talk in a higher education learning institution, my former school. The focus of my presentation was centered on Trading Psychology and Risk Management as … Continue reading Forex Conference held at Kenyatta University.
The year started with a bang after an invitation which was long overdue to speak to Kenyatta University students on what it takes to be a successful Forex trader. It was really great to have the talk in a higher education learning institution, my former school. The focus of my presentation was centered on Trading Psychology and Risk Management as … Continue reading Forex Conference held at Kenyatta University. - Diversification
 Diversification is crucial to building a long-lasting portfolio. Just like in most team-based sports, we must build a solid defense against potential attacks. In this case, diversification can help us stay invested in the market when we otherwise would have cashed out. Diversification also helps us remain disciplined during times when the market seems to be going up every single … Continue reading Diversification
Diversification is crucial to building a long-lasting portfolio. Just like in most team-based sports, we must build a solid defense against potential attacks. In this case, diversification can help us stay invested in the market when we otherwise would have cashed out. Diversification also helps us remain disciplined during times when the market seems to be going up every single … Continue reading Diversification - Final Top 10 Forex Literature Covered in 2017.
 Finally, this remarkable woman has some interesting stories. Those that keep you glued to your screen, you can’t catch a break. Kathy Lien in her book Millionaire Traders, How Everyday People are Beating Wall Street at its own Game will give you valuable lessons you can employ in your trading journey. This is a very good read for new traders. … Continue reading Final Top 10 Forex Literature Covered in 2017.
Finally, this remarkable woman has some interesting stories. Those that keep you glued to your screen, you can’t catch a break. Kathy Lien in her book Millionaire Traders, How Everyday People are Beating Wall Street at its own Game will give you valuable lessons you can employ in your trading journey. This is a very good read for new traders. … Continue reading Final Top 10 Forex Literature Covered in 2017. - My top 10 Forex Literature covered in 2017. (Part 2)
 Fooled by Randomness by Nassim Taleb one of the guys who made a killing during the 2008 global financial crisis completely takes my mind to a new planet. I like to think of Taleb as a contrarian. What that means is that he has no problem buying while all the talking heads are screaming sell. He is confident about the … Continue reading My top 10 Forex Literature covered in 2017. (Part 2)
Fooled by Randomness by Nassim Taleb one of the guys who made a killing during the 2008 global financial crisis completely takes my mind to a new planet. I like to think of Taleb as a contrarian. What that means is that he has no problem buying while all the talking heads are screaming sell. He is confident about the … Continue reading My top 10 Forex Literature covered in 2017. (Part 2) - My top 10 Forex Literature covered in 2017. (Part 1)
 Disclaimer, this article is in no way a marketing tool for the authors mentioned, rather my take home lessons from the knowledge I have gathered from reading their book material cover to cover. I hope you grab one of these books and read it for yourself. After all, ignorance is pretty damn ugly. I’m going to start with my current … Continue reading My top 10 Forex Literature covered in 2017. (Part 1)
Disclaimer, this article is in no way a marketing tool for the authors mentioned, rather my take home lessons from the knowledge I have gathered from reading their book material cover to cover. I hope you grab one of these books and read it for yourself. After all, ignorance is pretty damn ugly. I’m going to start with my current … Continue reading My top 10 Forex Literature covered in 2017. (Part 1) - ARE YOU READY FOR A FOREX COMPETITION IN KENYA?The beauty about forex trading is that you are given a chance by the markets to take what you believe is at your disposal and financially empower yourself regardless of your level of education, background, race, age, gender or any other criteria used to determine who is best for certain careers or other professions. Sylvia’s Traders Lounge is delighted to … Continue reading ARE YOU READY FOR A FOREX COMPETITION IN KENYA?
- TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (002)The following is an update of previous charts discussed earlier on this month with Sylvia’s Traders Lounge members. Of key importance is the emphasis to Swing Trading, Trading Chart Patterns and Technical Analysis. Keep following the series from time to time since we are working with a long term perspective. Gold. No trades initiated. Sylvia’s Traders Lounge members are long-term … Continue reading TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (002)
- What is my risk tolerance?
 Every financial advisor you consult with will always have one thing in mind. What is my client’s risk tolerance? I am sure you have heard this term thrown around, without possessing any specific definition to it. Business Dictionary defines risk as, “The probability that an actual return on an investment will be lower than the expected return.” What does that … Continue reading What is my risk tolerance?
Every financial advisor you consult with will always have one thing in mind. What is my client’s risk tolerance? I am sure you have heard this term thrown around, without possessing any specific definition to it. Business Dictionary defines risk as, “The probability that an actual return on an investment will be lower than the expected return.” What does that … Continue reading What is my risk tolerance? - MONEY
 A couple of days ago, a friend baptized me “dollar girl”, so I might as well do a piece on this once and for all. They say money won’t buy you happiness, think again because they went shopping at the wrong stores. Money is good. The lack of it is what makes people evil, thugs, murderers, and jerks. Ask yourself, … Continue reading MONEY
A couple of days ago, a friend baptized me “dollar girl”, so I might as well do a piece on this once and for all. They say money won’t buy you happiness, think again because they went shopping at the wrong stores. Money is good. The lack of it is what makes people evil, thugs, murderers, and jerks. Ask yourself, … Continue reading MONEY - Boring Stuff, But Gold.
 This is usually the part where I lose a few of you. Don’t worry, I feel the same way you do. Reading through columns and rows filled with numbers and abbreviated nonsense is not a good way to pass time. Still, I will share a well-kept industry secret with you. Most Fund Managers today do not bother to read financial … Continue reading Boring Stuff, But Gold.
This is usually the part where I lose a few of you. Don’t worry, I feel the same way you do. Reading through columns and rows filled with numbers and abbreviated nonsense is not a good way to pass time. Still, I will share a well-kept industry secret with you. Most Fund Managers today do not bother to read financial … Continue reading Boring Stuff, But Gold. - TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (001)I remember sharing a funnel topping formation of the dollar with a friend which reached its highest peak after Trump’s election. Ever since then, the dollar has been falling. One would have expected commodities to rally, for instance the inversely correlated major commodities like Crude and Gold to rally. In fact, the gold rally that began at the end of … Continue reading TECHNICAL ANALYSIS (001)
- Day 37 of #222daysofforexeducation . The difference between investing in the Stock markets and Forex trading
 Most of you have heard of Warren Buffet, the Stock market guru. I like his mantra, “If I don’t understand it, I won’t buy it”. Investing in the stock markets is simply becoming a shareholder in a company that is registered with the market regulators of that particular country. For example, regulation in the Kenyan market is done by the … Continue reading Day 37 of #222daysofforexeducation . The difference between investing in the Stock markets and Forex trading
Most of you have heard of Warren Buffet, the Stock market guru. I like his mantra, “If I don’t understand it, I won’t buy it”. Investing in the stock markets is simply becoming a shareholder in a company that is registered with the market regulators of that particular country. For example, regulation in the Kenyan market is done by the … Continue reading Day 37 of #222daysofforexeducation . The difference between investing in the Stock markets and Forex trading - (no title)
- Where can I research stocks?
 Back in the days it was extremely complicated to research information about a particular company. You had to go to the library and sort through thousands of microfiche in order to get information that was already 6 months to a year old. With the internet revolution, finding information has become child’s play. The flow of information is instantaneous and easily … Continue reading Where can I research stocks?
Back in the days it was extremely complicated to research information about a particular company. You had to go to the library and sort through thousands of microfiche in order to get information that was already 6 months to a year old. With the internet revolution, finding information has become child’s play. The flow of information is instantaneous and easily … Continue reading Where can I research stocks? - Profitable trading has to be effortless.
 Don’t get me wrong, I did not say easy, I said effortless. Trading is not easy as those who try to sell you systems portray. However, profitable trading has to be effortless. It is backed up by years of experience in a market niche that you are well conversant with and a trading style that suits your personality. You’ve got … Continue reading Profitable trading has to be effortless.
Don’t get me wrong, I did not say easy, I said effortless. Trading is not easy as those who try to sell you systems portray. However, profitable trading has to be effortless. It is backed up by years of experience in a market niche that you are well conversant with and a trading style that suits your personality. You’ve got … Continue reading Profitable trading has to be effortless. - WOMAN, LIBERATE YOURSELF. (PART 2)
 At some point in my life, I found myself in a classroom as the only African Woman. The other lady was from Russia. The rest were all male, including the professors and supervisors. Being a woman in this case did not give me an edge, it just meant I was different. That I have something to bring to the table, … Continue reading WOMAN, LIBERATE YOURSELF. (PART 2)
At some point in my life, I found myself in a classroom as the only African Woman. The other lady was from Russia. The rest were all male, including the professors and supervisors. Being a woman in this case did not give me an edge, it just meant I was different. That I have something to bring to the table, … Continue reading WOMAN, LIBERATE YOURSELF. (PART 2) - One on One personalized Forex Coaching and Lifetime Mentorship.
 I often look at how the markets favor the bold and really, the only difference between those who are good at this game and those who are barely getting by is founded on the basic principle of your knowledge and experience. It is therefore paramount to get grounded and understand the nature of the markets prior to getting your head … Continue reading One on One personalized Forex Coaching and Lifetime Mentorship.
I often look at how the markets favor the bold and really, the only difference between those who are good at this game and those who are barely getting by is founded on the basic principle of your knowledge and experience. It is therefore paramount to get grounded and understand the nature of the markets prior to getting your head … Continue reading One on One personalized Forex Coaching and Lifetime Mentorship. - WOMAN, LIBERATE YOURSELF
 Today is not 8th March (International Women’s Day), but I want to do a piece to all the young girls on their way to being young adults and finally graduating to womanhood. I speak to all the girls with an African dream of excelling at their studies because education does open your eyes to the infinite world of opportunities. Be … Continue reading WOMAN, LIBERATE YOURSELF
Today is not 8th March (International Women’s Day), but I want to do a piece to all the young girls on their way to being young adults and finally graduating to womanhood. I speak to all the girls with an African dream of excelling at their studies because education does open your eyes to the infinite world of opportunities. Be … Continue reading WOMAN, LIBERATE YOURSELF - Day110 of #222daysofforexeducation. Use Common Sense
 Building on to the discussion topic for yesterday, it’s important to write a piece on common sense, and this applies to everyone, whether you’re a trader or not, but I have to do it. Economics is built on theories, Keynesian models and so forth. I don’t want to get into much details. The same theories have justified the use of … Continue reading Day110 of #222daysofforexeducation. Use Common Sense
Building on to the discussion topic for yesterday, it’s important to write a piece on common sense, and this applies to everyone, whether you’re a trader or not, but I have to do it. Economics is built on theories, Keynesian models and so forth. I don’t want to get into much details. The same theories have justified the use of … Continue reading Day110 of #222daysofforexeducation. Use Common Sense - Is This a Good Company?
 In the rare occasion, I find myself at a dinner party. Shortly after introducing myself and exchanging pleasantries. The question always arises as soon as I share my profession. What do you think about Apple? Is Microsoft still a good company? What about Snapchat? Or Facebook? Is Bank of America a good bank to invest in? Is this a good … Continue reading Is This a Good Company?
In the rare occasion, I find myself at a dinner party. Shortly after introducing myself and exchanging pleasantries. The question always arises as soon as I share my profession. What do you think about Apple? Is Microsoft still a good company? What about Snapchat? Or Facebook? Is Bank of America a good bank to invest in? Is this a good … Continue reading Is This a Good Company? - Can you Really Beat The Market?
 Before we get into what it takes to make money in the stock market, and how. We must ask ourselves, “Can we beat the market?” The so-called “professionals” will most likely tell you that you have no chance in competing against them and consistently beat the market. For the most part, they recommend you put your money into a Mutual … Continue reading Can you Really Beat The Market?
Before we get into what it takes to make money in the stock market, and how. We must ask ourselves, “Can we beat the market?” The so-called “professionals” will most likely tell you that you have no chance in competing against them and consistently beat the market. For the most part, they recommend you put your money into a Mutual … Continue reading Can you Really Beat The Market? - Leaving The 9-5
 I still recall February 2015 like it was yesterday. One early morning, I rise up to beat the Thika Road traffic madness so that I can be in the office by 8:00am as is expected of every employee. That Tuesday mid morning, the PA to our then Managing Director steps into my office in the middle of a meeting and … Continue reading Leaving The 9-5
I still recall February 2015 like it was yesterday. One early morning, I rise up to beat the Thika Road traffic madness so that I can be in the office by 8:00am as is expected of every employee. That Tuesday mid morning, the PA to our then Managing Director steps into my office in the middle of a meeting and … Continue reading Leaving The 9-5 - PASSION
 Day 9 of #222daysofforexeducation I don’t want to sound cliché, but you can either be passionate about trading, or don’t do it at all. About 1% of market participants in the markets are successful, do not factor in the market makers, the big corporate manipulators such as Goldman Sachs & JP Morgan just to mention as examples. Also, do not … Continue reading PASSION
Day 9 of #222daysofforexeducation I don’t want to sound cliché, but you can either be passionate about trading, or don’t do it at all. About 1% of market participants in the markets are successful, do not factor in the market makers, the big corporate manipulators such as Goldman Sachs & JP Morgan just to mention as examples. Also, do not … Continue reading PASSION - My Forex Journey Part 2
 Long story short, I attended a seminar from one guy, Greg Secker from the United Kingdom. He calls himself a wealth coach due to his long term career in Forex Trading but no offense, the three hour session was nothing more than a marketing campaign for his trading company. He literally showed us on screen how he would make $40,000 … Continue reading My Forex Journey Part 2
Long story short, I attended a seminar from one guy, Greg Secker from the United Kingdom. He calls himself a wealth coach due to his long term career in Forex Trading but no offense, the three hour session was nothing more than a marketing campaign for his trading company. He literally showed us on screen how he would make $40,000 … Continue reading My Forex Journey Part 2 - My Forex Journey Part 1
 My Forex journey goes way back in early 2014, I had just graduated from Kenyatta University with a degree in Bachelor of Commerce with a major in Finance. I had got an accounting role in a local media startup which was later shut down due to the digital migration in 2015 (story for another day). During the one year that … Continue reading My Forex Journey Part 1
My Forex journey goes way back in early 2014, I had just graduated from Kenyatta University with a degree in Bachelor of Commerce with a major in Finance. I had got an accounting role in a local media startup which was later shut down due to the digital migration in 2015 (story for another day). During the one year that … Continue reading My Forex Journey Part 1
